- ▶ Accelerating improvement in corporate structure focusing on new businesses beyond smartphones such as automotive, AI and servers
- - Focus on growth businesses such as servers and automotive with cutting-edge technologies such as ultra-small and ultra-high capacity
- - Aiming to reach KRW 1 trillion for automotive MLCCs in 2024
- ▶ Automotive MLCC market to grow from KRW 4 trillion in 2023 to KRW 9.5 trillion in 2028
Samsung Electro-Mechanics is preparing for the transition to future growth markets by improving its corporate structure in response to changes in the electronics industry.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics is expanding its existing IT business by continuously introducing new technologies and new products for MLCC, its core business, and developing core technologies. The company plans to focus on growth businesses such as servers and automotive based on the technology it has acquired in the IT field.
Specifically, it aims to achieve KRW 1 trillion in automotive MLCC sales in 2024 through expanding its automotive product lineup and differentiated technology.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics also plans to aggressively target industrial product markets such as AI servers and robots for factory automation, which are emerging megatrend markets, based on its high-reliability technology for automotive and ultra-high-capacity technology for IT.
□ MLCC, Advanced Technology as Thin as a Human Hair
MLCC (Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitor) is a component that stores electricity and stably supplies electricity to active components such as semiconductors (APs, ICs) as needed to enable semiconductors to operate smoothly. It also plays a role in eliminating signal interference (noise) in electronic products.
MLCCs are used not only in smartphones, but also in products containing semiconductors and electronic circuits, such as televisions, home appliances, and electric vehicles.
The size of the product varies from 0.4mm*0.2mm (the thickness of a human hair is about 0.3mm) to 5.7mm*5.0mm, which is thinner than a human hair and barely visible to the naked eye. The latest smartphones contain about 1,000 and electric vehicles contain about 18,000 to 20,000.
Although it is the smallest electronic component, it is a high-tech product with 500~600 layers of dielectric and electrodes inside and is a high-value component worth hundreds of millions of won when filled into a 300ml wine glass.
□ MLCCs Require the Most Sophisticated Technologies at the Micro Level
MLCCs have a competitive advantage in that they can store large amounts of electricity while maintaining a small size, so it is essential to have particulate material technology such as dielectrics and manufacturing technology that can stack layers uniformly without interference.
At the nanotechnology level, the technology with the highest barrier to entry is semiconductors, but at the microtechnology level, MLCC has the highest barrier to entry.
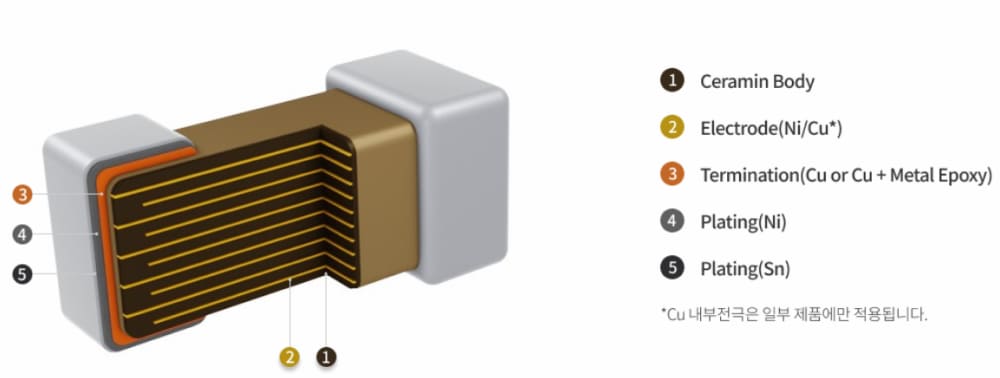
MLCCs are made by alternating layers of ceramic and metal (nickel). They are made by a process in which raw material with various additives is printed as thin as paper, stacked, cut to the required size, and heat treated like baking ceramics.
Which substances are added to the ceramic material and how much of each substance is added determines the characteristics of MLCCs. This ceramic raw material technology is the know-how of MLCC manufacturers and is the core technology of MLCC.
In addition, the more inner layers (ceramic and nickel) are stacked, the more electricity can be accumulated, so the micro-control manufacturing technology to make them thin and small is also very important.
Another factor that determines the quality of MLCCs is temperature, as the alternating layers of ceramic and nickel are baked at a high temperature of over 1,000°C. However, it is not easy to achieve the right temperature because ceramic and nickel bake at different temperatures.
Even if it is baked at the right temperature, it will not function properly if microscopic cracks are formed in the thin inner layer. Therefore, it is important to check the quality and appearance, including the electrical properties, for internal cracks, even if there is no visible damage on the outside.
[MLCC internal mimetic diagram]
□ MLCC “More than 10,000 MLCCs in a car”: The Scale of Automotive MLCCs is Growing
Although automotive MLCCs play a similar role to IT MLCCs, they are used in different environments than IT products and require a high level of reliability and durability because they are closely related to people’s lives.
For high-end automotive MLCCs, they need to operate reliably in extreme environments such as high temperatures (over 150℃) and low temperatures (minus 55℃), impact situations such as bending strength, and high humidity (85% humidity).
To meet the harsh testing environment of automobiles, materials that can withstand high temperature and high voltage must be developed, and microstructure design technologies that enhance vibration and moisture resistance must be employed.
Compared with IT products, automotive MLCCs require longer life, have higher technological difficulty, and take about three times longer to develop. They are also high-value-added products that cost more than three times as much.
Automotive MLCCs have high quality and manufacturing standards, such as the need to obtain AEC-Q200 certification, a reliability testing standard for automotive electronic components, and must pass strict inspection by each customer before they can be produced.
Electric vehicles are expected to grow at a double-digit rate in 2024 and hybrid vehicles, which are also growing steadily, are expected to have a positive impact on automotive MLCC demand, as they require up to twice as many MLCCs as internal combustion engines. At the same time, as the penetration rate of ADAS continues to increase, the adoption rate of Lv.2 and above is expected to exceed 40% in 2024, thus maintaining the high growth outlook for the automotive MLCC market.
According to market research firm TSR, the automotive MLCC market is expected to grow significantly from KRW 4 trillion in 2023 to KRW 9.5 trillion in 2028.
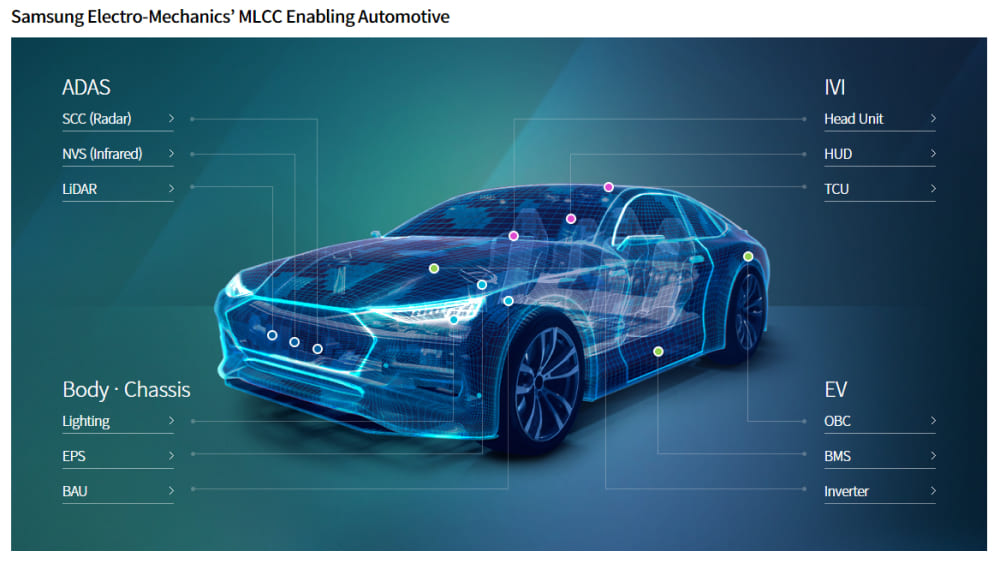

[Samsung Electro-Mechanics automotive MLCC application areas]
□ Samsung Electro-Mechanics Aims to Achieve KRW 1 trillion in Automotive MLCC Sales with Core Raw Material Technology
Samsung Electro-Mechanics is focusing on increasing the share of MLCCs for industrial and automotive applications. Samsung Electro-Mechanics began producing industrial and automotive MLCCs in 2016, and in 2018 the company built a dedicated automotive production line in Busan to promote the MLCC business in earnest.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics is strengthening its technological competitiveness by developing and manufacturing core raw materials for MLCCs in-house.
There are extremely few companies that can directly develop and internalize raw materials, the core technology of MLCC. Samsung Electro-Mechanics has recently built a new raw material plant exclusively for automotive purposes at its Busan business site and started operation from 2020.
Recently, Samsung Electro-Mechanics has been focusing on developing automotive MLCCs in line with the growth of the EV and ADAS markets. In particular, at the shareholders’ meeting held in March this year, Samsung Electro-Mechanics CEO Chang Duckhyun stated that the company has set a goal of achieving KRW 1 trillion in automotive MLCC sales.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics is expanding its automotive product lineup to ensure high capacity, bending strength, high temperature and high pressure based on the company’s competitiveness in material technology and process technology. In 2020, the company developed three types of MLCCs for automotive powertrain and two types of MLCCs for braking systems, and in 2021, it developed two types of MLCCs for ADAS. This is followed by an expansion of 13 types of MLCCs for automotive powertrain in 2022. In 2024, the company will expand its market share by introducing two types of MLCCs for ADAS with the world’s highest capacity in the 16V class and an automotive MLCC for electric vehicles that can withstand a high voltage of 1000V.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics operates its business sites in Suwon and Busan for R&D and production of new models and raw materials, and its production bases in Tianjin, China and the Philippines for mass production.